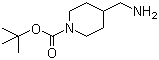
1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine is a protected amine derivative commonly used as an intermediate in organic synthesis and pharmaceutical chemistry. Its chemical structure consists of a six-membered piperidine ring substituted at the fourth position with a primary aminomethyl group and at the nitrogen atom with a tert-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) protecting group. The molecular formula of this compound is C11H22N2O2, and the Boc group is employed to temporarily mask the reactivity of the nitrogen atom, allowing selective reactions to occur at the free primary amine on the side chain. The compound is typically a white crystalline solid, moderately soluble in polar organic solvents, and stable under standard laboratory conditions.
The development of 1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine is part of the broader use of Boc-protected amines in synthetic chemistry. The Boc group was introduced in the 1950s as a convenient, removable protecting group for amines. Its stability under mild basic and neutral conditions, combined with its ability to be removed under acidic conditions, makes it ideal for multi-step synthesis where selective functionalization is required. In this compound, protection of the piperidine nitrogen ensures that reactions can be directed specifically toward the aminomethyl group without interference from the ring nitrogen.
Synthesis of 1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine generally begins with 4-(aminomethyl)piperidine as the starting material. The secondary amine on the ring nitrogen is treated with di-tert-butyl dicarbonate (Boc2O) in the presence of a mild base such as triethylamine or sodium bicarbonate. This reaction produces the Boc-protected derivative through formation of a carbamate linkage at the nitrogen atom. The reaction conditions, including solvent, temperature, and reaction time, are carefully controlled to ensure complete protection of the ring nitrogen while avoiding modification of the side-chain primary amine.
Chemically, 1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine retains the reactivity of the free primary amine on the side chain, allowing it to participate in various functionalization reactions. The aminomethyl group can undergo acylation, alkylation, reductive amination, and coupling reactions, enabling the introduction of diverse functional groups into the molecule. The Boc-protected nitrogen is inert under these conditions, providing selective reactivity and preventing undesired side reactions. Subsequent removal of the Boc group with acidic reagents such as trifluoroacetic acid regenerates the free secondary amine for further synthetic transformations.
The compound is widely used as a building block in medicinal chemistry. Its structural features make it suitable for incorporation into pharmacologically active molecules, including central nervous system agents, enzyme inhibitors, and receptor ligands. The piperidine ring contributes conformational rigidity and basicity, while the aminomethyl side chain provides a handle for attaching functional groups or linkers. The use of Boc protection ensures that multi-step syntheses can proceed efficiently without cross-reactivity, which is essential in the preparation of complex drug candidates.
From a practical perspective, 1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine is stable under ambient conditions but should be stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture uptake, which can lead to hydrolysis of the Boc group. It is soluble in polar aprotic solvents such as dimethylformamide, dichloromethane, and acetonitrile, facilitating its use in solution-phase reactions. Handling precautions include avoiding direct skin contact and inhalation of dust, as the compound may cause mild irritation.
Overall, 1‑Boc‑4-(aminomethyl)piperidine is a versatile, Boc-protected amine intermediate that allows selective chemical transformations in organic synthesis. Its combination of a protected ring nitrogen and a reactive aminomethyl side chain makes it valuable in multi-step synthetic strategies, particularly in the design and preparation of pharmacologically active compounds. The chemical stability, solubility characteristics, and selective reactivity of this compound continue to make it an important building block in modern medicinal chemistry and chemical research.
References
2023. Hit-to-lead optimization of amino-carboxamide benzothiazoles as LSD1 inhibitors. Medicinal Chemistry Research.
DOI: 10.1007/s00044-023-03046-6
|


















 GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details
GHS07;GHS09 Warning Details