Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| Shanghai Worldyang Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 13651600618 +86 (21) 5679-5779 | |||
 |
sales7777@worldyachem.com | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
 |
WeChat: 13651600618 | |||
 |
WhatsApp: +86 13651600618 | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink premium supplier since 2023 | ||||
| Hangzhou Verychem Science And Technology Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (571) 8816-2785 +86 13606544505 | |||
 |
lucy@verychem.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2004 | ||||
| chemBlink massive supplier since 2021 | ||||
| Classification | Chemical reagent >> Organic reagent >> Sulfonyl halide |
|---|---|
| Name | Nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride |
| Synonyms | Perfluoro-1-butanesulfonyl fluoride; Perfluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride |
| Molecular Structure | 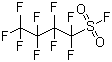 |
| Molecular Formula | C4F10O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 302.09 |
| CAS Registry Number | 375-72-4 |
| EC Number | 206-792-6 |
| SMILES | C(C(C(F)(F)S(=O)(=O)F)(F)F)(C(F)(F)F)(F)F |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 Calc.*, 1.75 g/mL (Expl.) |
|---|---|
| Melting point | -110 ºC (Expl.) |
| Boiling point | 64.2±35.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)*, 64 ºC (Expl.) |
| Flash point | -7.4±25.9 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.287 (Calc.)*, 1.3 (Expl.) |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
| Hazard Symbols |
 GHS05 Danger Details
GHS05 Danger Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Statements | H314 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Precautionary Statements | P260-P264-P280-P301+P330+P331-P302+P361+P354-P304+P340-P305+P354+P338-P316-P321-P363-P405-P501 Details | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Classification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Transport Information | UN 3265 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SDS | Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride is a perfluorinated sulfonyl fluoride widely used as a reactive reagent in organic synthesis, materials science, and chemical biology. It belongs to the class of perfluoroalkyl sulfonyl fluorides, which are characterized by a strongly electron-withdrawing perfluoroalkyl chain linked to a sulfonyl fluoride functional group. This combination confers high chemical reactivity together with thermal and chemical stability derived from the fully fluorinated carbon chain. The emergence of nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride is closely connected to the development of perfluorinated reagents in the second half of the twentieth century. Advances in fluorine chemistry demonstrated that perfluoroalkyl groups impart unique electronic and physicochemical properties, including strong inductive effects, hydrophobicity, and resistance to oxidative and thermal degradation. Sulfonyl fluorides were recognized as particularly useful functional groups because they are sufficiently stable for handling and storage, yet reactive enough to undergo selective substitution reactions with nucleophiles. The nonafluorobutyl variant was developed to combine these features with a shorter perfluoroalkyl chain than perfluorooctyl analogues, reducing persistence while maintaining strong electron-withdrawing character. Chemically, nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride consists of a C4 perfluoroalkyl chain attached to a sulfonyl fluoride moiety. The sulfur atom is in a high oxidation state, bonded to two oxygen atoms, one fluorine atom, and the perfluoroalkyl group. The sulfur–fluorine bond is polarized and activated by the adjacent sulfonyl group, making it susceptible to nucleophilic attack. This reactivity underlies the compound’s utility as a sulfonylating agent. At the same time, the perfluorinated carbon chain is chemically inert under most reaction conditions, serving primarily as an electronic and steric modifier. The primary application of nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride is as an electrophilic reagent for introducing the nonafluorobutanesulfonyl group into organic molecules. It reacts readily with alcohols, amines, and other nucleophiles to form sulfonate esters or sulfonamides. These derivatives are valuable as protecting groups, leaving groups, or intermediates in multistep syntheses. The resulting nonafluorobutanesulfonates often display excellent leaving-group ability, which can facilitate substitution or elimination reactions in synthetic sequences. In medicinal chemistry and chemical biology, sulfonyl fluorides have gained attention as covalent modifiers of enzymes and proteins. The sulfonyl fluoride group can react selectively with nucleophilic amino acid side chains, particularly serine, threonine, or lysine residues, under controlled conditions. Nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride and related compounds have therefore been explored as tools for enzyme inhibition, activity-based protein profiling, and mechanistic studies. The strong electron-withdrawing perfluoroalkyl group can tune the reactivity of the sulfonyl fluoride, allowing adjustment of reaction rates and selectivity. Nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride has also found use in materials science. Perfluoroalkyl sulfonates derived from this reagent can impart hydrophobic and oleophobic properties to surfaces and polymers. Incorporation of the nonafluorobutanesulfonyl group into polymer backbones or side chains can modify surface energy, chemical resistance, and thermal stability. Compared with longer-chain perfluoroalkyl analogues, the C4 chain offers a balance between performance and reduced molecular size, which has become increasingly important in response to environmental considerations associated with long-chain perfluoroalkyl substances. From a practical standpoint, nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride is typically handled as a moisture-sensitive liquid. It reacts with water to form the corresponding sulfonic acid, releasing hydrogen fluoride, so reactions are usually conducted under anhydrous conditions. Despite this sensitivity, it is sufficiently stable for routine laboratory use when proper precautions are taken. Overall, nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride represents an important example of a functional perfluorinated reagent whose discovery and application reflect broader developments in fluorine chemistry. Its combination of a reactive sulfonyl fluoride group with a chemically robust perfluoroalkyl chain has made it a versatile tool in organic synthesis, chemical biology, and materials science, illustrating how targeted molecular design can yield reagents with both practical utility and controlled reactivity. References 2025. Neurodevelopmental effects of exposure to environmentally relevant concentrations of perfluorooctane sulfonic acid (PFOS), perfluorobutanesulfonic acid (PFBS) and 6:2 chlorinated polyfluorinated ether sulfonate (6:2 Cl-PFESA) on larval zebrafish: Multi-omics and neuropathology perspective. Journal of Hazardous Materials. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138744 2025. Sensitive electrochemical sensor based on hybrid material F-doped carbon quantum dots (Cdots) and NiO nanoparticles: detection of ketoconazole in pharmaceutical formulations and tap water samples. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. DOI: 10.1007/s00216-025-06002-y |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for Nonafluorobutanesulfonyl fluoride |