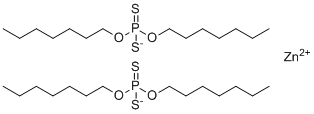
Phosphorodithioic acid O,O-di-C1-14-alkyl esters zinc salts are a class of organophosphorus compounds commonly used as anti-wear additives in lubricants. These compounds have a general molecular structure in which a zinc ion coordinates to the anionic phosphorodithioate groups, each containing two alkyl chains of 1 to 14 carbon atoms. The molecular formula varies depending on the alkyl chain length, but the core structure consists of Zn[(S2P(OR)2)]2, where R represents the alkyl group. They are typically yellow to amber viscous liquids or solids, soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and oils, but insoluble in water.
The discovery and industrial development of zinc dialkyldithiophosphates (ZDDPs) date back to the early 1940s when researchers were investigating organophosphorus compounds to reduce engine wear and friction. ZDDPs quickly became standard anti-wear and antioxidant additives in motor oils due to their ability to form protective films on metal surfaces under high pressure and temperature conditions. Their unique chemical composition allows them to react with metal surfaces to generate a thin tribofilm, preventing direct metal-to-metal contact and reducing mechanical wear.
Synthesis of phosphorodithioic acid O,O-di-C1-14-alkyl esters zinc salts generally involves the reaction of dialkyl phosphorodithioic acids with zinc oxide or zinc hydroxide. The dialkyl phosphorodithioic acids are themselves prepared by the reaction of phosphorus pentasulfide with alcohols in the presence of a base to form the O,O-dialkyl esters. Zinc salts are obtained by neutralizing the acidic esters with zinc oxide, resulting in the formation of the metal-coordinated phosphate complex. Reaction conditions, such as temperature, molar ratios, and solvent choice, are controlled to maximize yield and minimize decomposition.
Chemically, ZDDPs function as anti-wear and antioxidant agents due to the reactive phosphorus-sulfur moiety. Under high temperatures and pressures, the zinc dialkyldithiophosphate decomposes at the metal surface to form a thin, adherent layer of zinc polyphosphate and iron sulfide compounds. This layer acts as a sacrificial barrier to prevent metal-to-metal contact and oxidative damage. The alkyl chain length and branching influence solubility in base oils, thermal stability, and film formation properties, allowing formulation optimization for specific lubrication applications.
In practical applications, these zinc salts are widely used as multi-functional additives in engine oils, hydraulic fluids, gear oils, and other industrial lubricants. They reduce wear, prevent corrosion, and act as antioxidants, thereby extending the lifetime of mechanical systems. The compounds are also used in metalworking fluids and as stabilizers in certain polymer systems due to their anti-oxidative properties. Their performance depends on concentration, base oil type, and operating conditions such as temperature, load, and shear stress.
Physically, ZDDPs are stable under normal storage conditions but are sensitive to strong acids, bases, and oxidizing agents, which can degrade the phosphorus-sulfur bonds. Proper handling includes using gloves, protective clothing, and eye protection, as the compounds can cause skin or eye irritation. They are typically stored in airtight containers in a cool, dry environment to maintain chemical integrity.
Overall, phosphorodithioic acid O,O-di-C1-14-alkyl esters zinc salts are key organophosphorus additives in lubrication technology. Their combination of anti-wear, antioxidant, and corrosion-inhibiting properties, along with tunable alkyl chain characteristics, makes them indispensable in automotive, industrial, and machinery applications. The ability to form protective tribofilms on metal surfaces ensures the longevity and efficiency of mechanical systems under demanding conditions.
|



















 GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details
GHS05;GHS07;GHS09 Danger Details