Online Database of Chemicals from Around the World
| BOC Sciences | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 485-4226 | |||
 |
info@bocsci.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Creative Peptides | USA | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+1 (631) 624-4882 | |||
 |
info@creative-peptides.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2010 | ||||
| Chengdu Youngshe Chemical Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (28) 6232-8193 +86 17380623303 | |||
 |
caroline@youngshechem.com | |||
 |
Skype Chat | |||
 |
QQ chat | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2013 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2015 | ||||
| Natural Micron Pharm Tech Co., Ltd. | China | Inquire | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
+86 (0538) 535-2278 | |||
 |
info@nmpharmtech.com | |||
| Chemical manufacturer since 2012 | ||||
| chemBlink standard supplier since 2025 | ||||
| Classification | Biochemical >> Peptide |
|---|---|
| Name | 1-Acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine |
| Synonyms | Acetyltetrapeptide 11 |
| Molecular Structure | 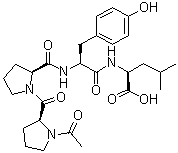 |
| Protein Sequence | PPYL |
| Molecular Formula | C27H38N4O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 530.61 |
| CAS Registry Number | 928006-88-6 |
| EC Number | 618-876-3 |
| SMILES | CC(C)C[C@@H](C(=O)O)NC(=O)[C@H](CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)NC(=O)[C@@H]2CCCN2C(=O)[C@@H]3CCCN3C(=O)C |
| Solubility | Very slightly soluble (0.34 g/L) (25 ºC), Calc.* |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.290±0.06 g/cm3 (20 ºC 760 Torr), Calc.* |
| Boiling point | 913.0±65.0 ºC 760 mmHg (Calc.)* |
| Flash point | 506.0±34.3 ºC (Calc.)* |
| Index of refraction | 1.582 (Calc.)* |
| * | Calculated using Advanced Chemistry Development (ACD/Labs) Software. |
|
1-Acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine is a synthetic tetrapeptide consisting of four amino acid residues arranged in a defined sequence, with an N-terminal acetyl modification. The peptide contains two consecutive proline residues, a tyrosine, and a leucine, conferring a combination of rigidity, polarity, and hydrophobicity. N-terminal acetylation is a common modification in synthetic peptides, enhancing stability against enzymatic degradation and influencing interactions with biomolecules. Such peptides are typically studied as model compounds for understanding structure–activity relationships, receptor interactions, and enzymatic specificity. The preparation of 1-acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine is facilitated by solid-phase peptide synthesis, a method that allows sequential coupling of protected amino acids with high fidelity. Proline residues, due to their cyclic structure, introduce conformational constraints that can affect the peptide’s secondary structure, while tyrosine contributes a phenolic side chain capable of hydrogen bonding and aromatic interactions. Leucine provides hydrophobic character, supporting peptide folding and stability in aqueous or membrane environments. The acetylation of the N-terminal proline not only protects against exopeptidase activity but can also mimic post-translational modifications observed in natural peptides, allowing more physiologically relevant studies. Chemically, the peptide exhibits features characteristic of short peptides: moderate solubility in aqueous solutions, susceptibility to proteolysis unless protected, and defined reactivity at its side chains. The presence of two proline residues in succession can induce turns or kinks in the backbone, affecting overall conformation and accessibility of other residues for interactions. Tyrosine, with its hydroxyl group, can participate in hydrogen bonding or undergo further derivatization, whereas leucine contributes to hydrophobic interactions that may stabilize peptide–protein complexes. Applications of 1-acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine are primarily in biochemical and biophysical research. It can serve as a model to investigate enzymatic specificity, particularly for peptidases recognizing proline-rich sequences. Studies using such tetrapeptides help elucidate the influence of sequence, stereochemistry, and terminal modifications on protease recognition and cleavage efficiency. In addition, the peptide may be employed in receptor-binding studies, as short sequences with defined residues often serve as ligands or probes to explore protein–peptide interactions. Analytically, the peptide functions as a reference standard in chromatographic and spectrometric assays. Its well-defined sequence, molecular weight, and stability allow precise calibration of methods for detecting and quantifying peptides. Such applications are critical in studies of peptide metabolism, synthetic efficiency, and degradation kinetics. The peptide’s chemical stability, conferred by acetylation and the specific residue composition, ensures reproducibility in experimental settings. Although 1-acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine is not used therapeutically, it exemplifies how short, chemically defined peptides facilitate fundamental research. By providing a controlled system with known sequence and modifications, researchers can dissect the role of specific residues, study enzyme interactions, and probe the effects of N-terminal capping on stability and biological activity. In summary, 1-acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine is a synthetically accessible tetrapeptide designed for experimental applications in peptide chemistry and molecular biology. Its combination of proline-induced conformational rigidity, functional side chains, and N-terminal acetylation makes it a versatile model for investigating enzymatic specificity, molecular interactions, and analytical characterization of peptides. References 2025. Full-cortex effect compound peptide. CN Patent. URL: CN-119454498-A 2025. High-concentration blue copper peptide and active peptide sustained and controlled release composition and preparation method thereof. CN Patent. URL: CN-119367224-A |
| Market Analysis Reports |
| List of Reports Available for 1-Acetyl-L-prolyl-L-prolyl-L-tyrosyl-L-leucine |